平面幾何(plane geometory)
点(point)
complexクラスがあればそれで代用してもいい。
演算子オーバーロードが無いと面倒すぎる。
法線ベクトルは複素数を考えればすぐわかる
import java.awt.geom.Point2D; static final double EPS = 1e-10; static boolean equal(double a, double b){ return Math.abs(a-b) < EPS; } // a == b static boolean less(double a, double b){ return a - b < -EPS; } // a < b static boolean leq(double a, double b){ return a - b < EPS; } // a <= b static boolean greater(double a, double b){ return less(b,a); } // a > b static boolean geq(double a, double b){ return leq(b,a); } // a >= b @SuppressWarnings("serial") public static class Point extends Point2D.Double implements Comparable<Point>{ //constructor public Point(double x, double y){ super(x,y); } public Point(Point p){ super(p.x, p.y); } //setter public final void set(double x, double y){ this.x = x; this.y = y; } public final void set(Point p){ this.x = p.x; this.y = p.y; } //norm public final double norm(){ return Math.sqrt( normsq() ); } public final double normsq(){ return x*x + y*y; } //addition, subtraction, multiplication, division public final Point add(Point p){ return new Point( x + p.x, y + p.y ); } public final Point sub(Point p){ return new Point( x - p.x, y - p.y ); } public final Point mul(double k){ return new Point( k*x, k*y ); } public final Point div(double k){ return new Point( x/k, y/k ); } //unit vector public final Point unit(){ return this.div(this.norm()); } //a normal unit vector(±normalVector()) public final Point normalV(){ double d = this.norm(); return new Point(-y/d, x/d); } //compareTo ascending order. priority 1. The x coordinate, 2. The y coordinate. @Override public final int compareTo(Point o){ return (this.x != o.x) ? java.lang.Double.compare(this.x, o.x) : java.lang.Double.compare(this.y, o.y); } //... abbr. } //class Point
内積(inner product), 外積(outer product)
内側・外側の判定や、方向の判定に使う
内積(inner product)
外積(outer product)
スカラー3重積(scalar triple product)
複素数クラスがあるなら、
で求められる。
//Instance Method of class Point /** * Returns outer product |a||b|sinθ. a = this, b = p.<br> * @param p * @return |a||b|sinθ */ public final double cross(Point p){ return x * p.y - y * p.x; } /** * Returns inter product |a||b|cosθ. a = this, b = p. * @param p * @return |a||b|cosθ */ public final double dot(Point p){ return x * p.x + y * p.y; }
ccw
3点の位置関係を求める。
3点が一直線上にないとき、反時計回り(counter clockwise)なら1, 時計回りなら(clockwise)なら-1を返す。
//Instance Method of class Point /** * Returns integer value that indicates positional relation of Points a(this point), b, and c.<br> * Positive return value indicates counter clockwise. * @param b Target Point 1 * @param c Target Point 2 * @return 1: ab → ac counter clockwise<br> * -1: ab → ac clockwise<br> * 2: (c--a--b or b--a--c) on line<br> * -2: (a--b--c or c--b--a) on line (b≠c, includes a=b)<br> * 0: (a--c--b or b--c--a) on line (includes c=b, a=c, a=b=c) */ public final int ccw(Point b, Point c) { Point ab = b.sub(this); Point ac = c.sub(this); if (greater(ab.cross(ac), 0)) return +1; // counter clockwise if (less(ab.cross(ac), 0)) return -1; // clockwise if (less(ab.dot(ac), 0)) return +2; // (c--a--b or b--a--c) on line if (less(ab.normsq(), ac.normsq())) return -2; // (a--b--c or c--b--a) on line (b≠c, includes a=b) return 0; // (a--c--b or b--c--a) on line (includes c=b, a=c, a=b=c) }
多角形が点 を包含しているかどうかの判定
を包含しているかどうかの判定
点Pからxの正方向への半直線が多角形の辺に偶数回交わっていれば、点Pを包含、奇数回なら包含していないことが分る。
多角形の辺を取り出し、それと点Pからxの正方向への半直線が交わっているかどうか、
すなわち、点Pが辺の右側にあるか、左側にあるかは、基本的にcross()だけで求まる。
※xの正方向への半直線が多角形の頂点に交わる時、合計交差回数が偶数回になるように、境界条件に注意する。
,
※が
より下にあるときと考えると、
は右側
は左側
は平行かつ異なる向きなので
は、
を内分する位置にある。
また、が
の上側または下側にあるかは、
のy座標で分かる。

/** * Tests whether polygon[0]→polygon[1]→...→polygon[polygon.length-1]→polygon[0] contains point p or not. * @param Polygon vertex set of target polygon * @param p target point * @return true -> polygon contains p. false -> polygon doesn't contain p. */ public static boolean contains(Point[] polygon, Point p) { boolean in = false; for (int i = 0, n = polygon.length; i < n; ++i) { Point a = polygon[i].sub(p), b = polygon[(i+1)%n].sub(p); if (a.y > b.y){ Point temp = b; b = a; a = temp; } if (a.y <= 0 && 0 < b.y) //点pからxの正方向への半直線が多角形の頂点をとおるとき、最終的に交差数を偶数回にするためどちらかを<=ではなく、<にする if (a.cross(b) < 0) in = !in; //=0 -> a//b -> on if (equal(a.cross(b), 0) && leq(a.dot(b), 0)) return true; //on edge } return in; //in out }
多角形の面積
ただし、
下図の緑の台形の面積を足して、赤の台形の面積を引くことで青の多角形の面積が求まる。
多角形のが左回りか右回りかで正負が変わってくるので絶対値をとる。
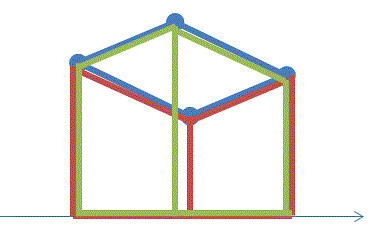
/** * Returns the area of a polygon.<br> * n = polygon.length, polygon[0]→polygon[1]→...→polygon[n-1]→polygon[0]<br> * O(n)<br> * @param polygon(n>=3) * @return The area of a polygon */ public static double square(Point[] polygon){ int n = polygon.length; double res = 0.0; for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i){ Point cur = polygon[i], next = polygon[(i+1)%n]; res += (cur.x + next.x)*(cur.y - next.y); } return Math.abs(res/2.0); }
凸多角形(convex polygon)の判定
ccwで常に時計回りか常に反時計回りなら凸多角形。
/** * Tests whether polygon[0]→polygon[1]→...→polygon[polygon.length-1]→polygon[0] is convex polygon or not. * ※ Assumes that (adjacency) 3 points on same line doesn't exists. * @param polygon vertex set of target polygon * @return true -> polygon is convex. false -> not convex. */ public static final boolean isConvex(Point[] polygon) { int n = polygon.length; if(n < 3) return false; //clockwise at all-points or counter clockwise at all-points → true int sign = polygon[n-1].ccw(polygon[0], polygon[1]); for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i){ int prev = (i + n-1)% n; int curr = i; int next = (i + 1) % n; if (sign != polygon[prev].ccw(polygon[curr], polygon[next])) return false; } return true; }
凸包(convex hull)
頂点集合の全ての頂点を包含する最小の凸形状(任意の2頂点間の線分が包含されている形状)を凸包という。
Andrewのアルゴリズムが簡単で分かりやすい(GrahamScanをccwで置き換えるやり方)。
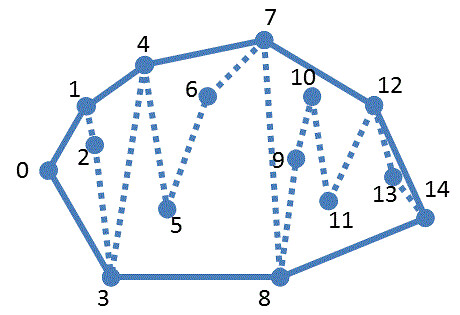
- Vをx座標でソート(x座標が等しければ、y座標で決める)する→
- 上凸の候補集合
, 下凸の候補集合
と初期化する。
- foreach(
)
- while(
) do
- foreach(
)
- while(
) do
- return
※の
番目の要素をそれぞれ
で表す。
※は
から
が反時計回りの位置にあるなら正、時計回りの位置にあるなら負。
ソートで]探索で
なので、計算量は
下の実装では、候補集合をの2倍のサイズの配列で確保していて、上凸、下凸で共用している。
また、上の説明で言うをループの最初で入れずに、後で入れるようになっている。
上凸を求めるコードのtによる条件は上の説明でのに相当する。
※下凸の計算を終えた時点でres[k-1]に下凸の終点(一番右の頂点V[n-1])が入っている。
public static final Point[] convexHull(Point[] V) { int n = V.length; if(n < 3) return null; Arrays.sort(V); //sorts based on x coordinate in ascending order int k = 0; //index of C Point[] C = new Point[2*n]; /* lower-hull */ for(int i = 0; i < n; C[k++] = V[i++]) while(k >= 2 && C[k-2].ccw(C[k-1], V[i]) <= 0) --k; /* upper-hull */ // t=|lower-hull|+1 for(int i = n-2, t = k + 1; i >= 0; C[k++] = V[i--]) while(k >= t && C[k-2].ccw(C[k-1], V[i]) <= 0) --k; return Arrays.copyOf(C, k-1); //C[k-1] is start point of lower-hull. }