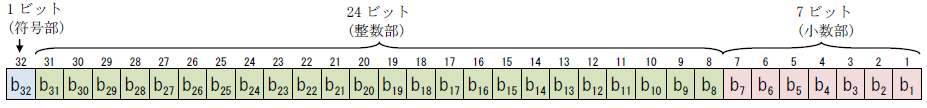Aka-beko and 40 Thieves(AOJ No. 0266), Triangle of Blocks(AOJ No. 0267), Kongo Type(AOJ No. 0268), East Wind(AOJ No. 0269), Modular Query(AOJ No. 0270)
コード
import java.util.*; public class aoj0266 { static final Scanner stdin = new Scanner(System.in); enum City { A, B, X, Y, Z, W, D; static City path[][] = { {X, Y}, {Y, X}, {D, Z}, {X, D}, {W, B}, {B, Y}, {D, D} }; } public static void main(String[] args) { while (true) { char[] str = stdin.next().toCharArray(); if (str[0] == '#') break; int pos = City.A.ordinal(); for (char c : str) pos = City.path[pos][c - '0'].ordinal(); System.out.println(pos == City.B.ordinal() ? "Yes" : "No"); } } }
Triangle of Blocks(AOJ No. 0267)
ブロックの並びが与えられたとき
- 一番下のブロックを取り除く
- 取り除いたブロックを右端に縦に並べる。
- 隙間がある場合は右につめる
という操作を何回繰り返せば段差1の階段状になるかを答える。完成系にならない場合または操作回数が10,000を超える場合はNAと答える。
階段の高さをkとしたときブロックの総数がk×(k+1)/2でないと完成系はつくれない。
コード
import java.util.*; public class aoj0267 { static final Scanner stdin = new Scanner(System.in); static final int LIMIT = 10000, N = 100; @SuppressWarnings("serial") static final List<Integer> TRI = new ArrayList<Integer>(N){ { add(-1); for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i) add((i+1)*(i+2)/2); } }; public static void main(String[] args) { while (true) { int n = stdin.nextInt(), s = 0; if (n == 0) break; List<Integer> l = new ArrayList<Integer>(n); for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { l.add(stdin.nextInt()); s += l.get(i); } int i = -1; if (TRI.contains(s)) { for (i = 0; i <= LIMIT && !check(l); ++i) { int sz = l.size(); for (int j = 0; j < sz; ++j) l.set(j, l.get(j)-1); int idx = -1; while((idx = l.indexOf(0)) != -1) l.remove(idx); l.add(sz); } } System.out.println(i > LIMIT ? -1 : i); } } static boolean check(List<Integer> l) { for (int i = 0; i < l.size(); ++i) if (l.get(i) != i+1) return false; return true; } }
コード
BigDecimal使わなくてもいいかも
import java.math.BigDecimal; import java.util.*; public class aoj0268 { static final Scanner stdin = new Scanner(System.in); static final BigDecimal divisor = new BigDecimal((1<<7)); public static void main(String[] args) { int n = stdin.nextInt(); while (n-- > 0) { long x = Long.parseLong(stdin.next(), 16); StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder((x&0x80000000) == 0 ? "" : "-"); BigDecimal d = new BigDecimal((x&0x7fffffff)); sb.append(d.divide(divisor).toString()); if (sb.indexOf(".") == -1) sb.append(".0"); System.out.println(sb.toString()); } } }
East Wind(AOJ No. 0269)
座標(0,0)に私の梅の木があり、
まず、H個の家、U個の(私のではない)梅の木、M個の松の木、S個の桜の木の座標と、梅・桃・桜の香りが広がる角度du、dm、dsが与えられる。
風の強さaと風の吹く方向wが与えられたとき、図のように香りが広がる。
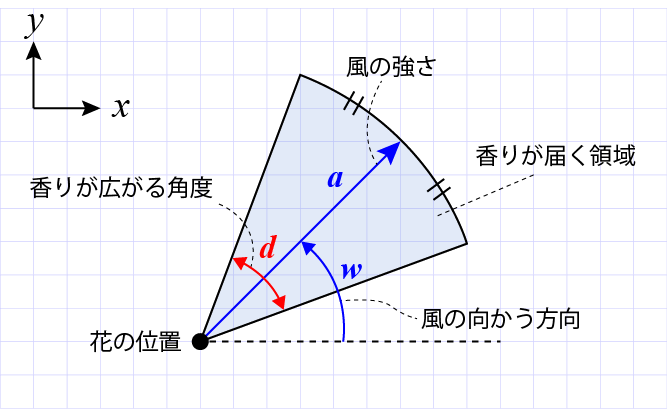
R日分の風の情報(風の強さ+風の方向)が与えられたとき、私の梅の木の香りだけがとどく日数が最も多い家を答える。
候補が多い場合は、家を昇順にならべて答える。
制約
1 ≤ H,R ≤ 100)
- 1,000 ≤ 座標 ≤ 1,000 以下の整数である。
0 ≤ w < 360, 1 ≤ du,dm,ds < 180 (単位は°)
0 < a ≤ 100
0 ≤ U, M, S ≤ 10
アルゴリズム
香りの境界の方向ベクトルを
木から家への方向ベクトルを
としたとき、距離がa以内かつ、が
からccw,
からcwの位置にあれば香りがその家にとどく。
ccwかcwかは外積の符号で決めればいい。
コード
Math.toRadiansの存在に初めて気付いた。
import java.awt.geom.Point2D; import java.util.*; public class aoj0269 { static final Scanner stdin = new Scanner(System.in); public static void main(String[] args) { while (true) { int H = stdin.nextInt(), R = stdin.nextInt(); if ((H|R) == 0) break; Point[] house = new Point[H]; for (int i = 0; i < H; ++i) house[i] = new Point(stdin.nextDouble(), stdin.nextDouble()); T[][] t = new T[3][]; t[0] = new T[stdin.nextInt()]; t[1] = new T[stdin.nextInt()]; t[2] = new T[stdin.nextInt()]; int[] ds = {stdin.nextInt(), stdin.nextInt(), stdin.nextInt()}; for (int i = 0; i < t.length; ++i) for (int j = 0; j < t[i].length; ++j) t[i][j] = new T(stdin.nextInt(), stdin.nextInt(), ds[i]); T myU = new T(0, 0, ds[0]); int freq[][] = new int[H][2]; for (int i = 0; i < H; ++i) freq[i][1] = i+1; for (int k = 0; k < R; ++k) { int w = stdin.nextInt(), a = stdin.nextInt(); myU.input(w, a); for (int i = 0; i < t.length; ++i) for (int j = 0; j < t[i].length; ++j) t[i][j].input(w, a); LOOP: for (int h = 0; h < H; ++h) { if (!myU.contain(house[h])) continue; for (int i = 0; i < t.length; ++i) for (int j = 0; j < t[i].length; ++j) if (t[i][j].contain(house[h])) continue LOOP; freq[h][0]++; } } Arrays.sort(freq, new Comparator<int[]>(){ @Override public int compare(int[] o1, int[] o2) { return o1[0] != o2[0] ? o2[0] - o1[0] : o1[1] - o2[1]; } }); StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); if (freq[0][0] == 0) { sb.append("NA"); } else { sb.append(freq[0][1]); int m = freq[0][0]; for (int i = 1; i < H; ++i) { if (freq[i][0] == m) sb.append(" ").append(freq[i][1]); else break; } } System.out.println(sb.toString()); } } static class T { Point[] tri = new Point[3]; int d, a; T(int x, int y, int d) { this.d = d; tri[0] = new Point(x, y); } void input(int w, int a) { this.a = a; double theta = Math.toRadians(w-d/2); tri[1] = new Point(Math.cos(theta), Math.sin(theta)); theta = Math.toRadians(w+d/2); tri[2] = new Point(Math.cos(theta), Math.sin(theta)); } boolean contain(Point p) { return leq(p.distance(tri[0]), a) && leq(0, tri[1].cross(p.sub(tri[0]))) && leq(0, p.sub(tri[0]).cross(tri[2])); } } public static final double EPS = 1e-9; public static boolean leq(double a, double b){ return a - b < EPS; } // a <= b @SuppressWarnings("serial") public static class Point extends Point2D.Double { public Point(double x, double y){ super(x,y); } public final Point sub(Point p){ return new Point( x - p.x, y - p.y ); } public final double cross(Point p){ return x * p.y - y * p.x; } } //class Point }
Modular Query(AOJ No. 0270)
N個の整数ci, とQ個の整数(クエリ)qjが与えられ、各クエリごとにを答える。
制約
2 ≤ N ≤ 300,000
2 ≤ Q ≤ 100,000
1 ≤ ci, q_j ≤ 300,000
アルゴリズム
cを入力した後、LB[k] = lower_bound(c, c+N, k-1)を求めとく(kより小さい最大のci).
qが与えられると、LB[max(c)]からLB[1]の方向へ探索する。
ci = kだったとき、剰余p = ci % qjを求めて解答候補を更新(最大値を保存)する。
次の探索位置は、k-pより小さい最大のci。
k' = LB[k-p]の位置にスキップして探索する。
これを繰り返すとで求まる。
qが大きく、ciが密集しているときに効率がよくなる。
コード
import java.util.*; public class aoj0270 { static final Scanner stdin = new Scanner(System.in); static final int N = 300001, LB[] = new int[N]; static final boolean C[] = new boolean[N]; public static void main(String[] args) { int n = stdin.nextInt(), Q = stdin.nextInt(), m = -1; for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { int c = stdin.nextInt(); C[c] = true; m = Math.max(m, c); } for (int i = 0, j = 0; i < m+1; ++i) { LB[i] = j; if (C[i]) j = i; } while (Q-- > 0) { int q = stdin.nextInt(), ans = 0, p; for (int i = m; i > 0; i = LB[i-p]) { p = i % q; ans = Math.max(ans, p); if (i - p < 0) break; } System.out.println(ans); } } }